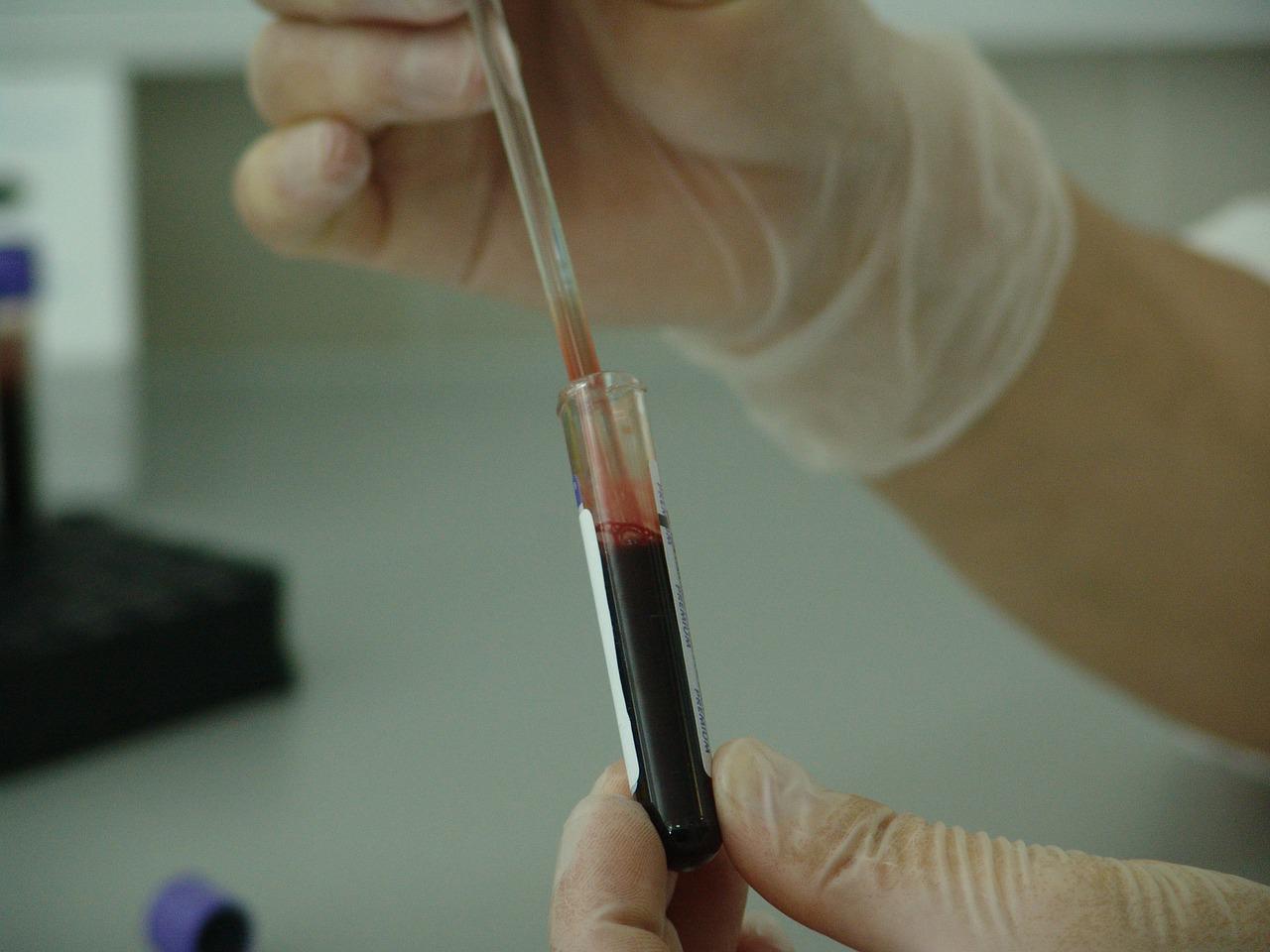
New Prenatal Genetic Screens Pose Underappreciated Ethical Dilemmas
By Daniel Navon,
Scientific American
| 05. 05. 2022
Imagine you are an expectant parent. Just a couple of months into your pregnancy, you opt for an easy genetic screen. A result comes back: the fetus is likely missing a chunk of DNA at site 11.2 on the long arm of the 22nd chromosome—a variant associated with serious medical and developmental issues.
You go online and learn that at least 1 in 4,000 people have this “22q11.2” microdeletion, but the true figure may be much higher. You read about 22q11.2 deletion syndrome’s 180-plus symptoms, including heart malformations, hypocalcemia, intellectual disability, autism and schizophrenia. You discover the bewildering treatment guidelines, the specialist clinics scattered throughout the country, and the vibrant patient advocacy movement spearheaded by the International 22q11.2 Foundation.
Yet the same pathogenic variant—a genetic change or “mutation” known to cause disease—has been found in people with much milder symptoms, and some who barely seem affected at all. No one can give you solid risk factors because our knowledge of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (also known as DiGeorge syndrome) is riddled with “ascertainment bias”: only people with telltale problems are...
Related Articles
By Anna Louie Sussman, The New York Times | 04.01.2025
When Noor Siddiqui was growing up, her mother developed retinitis pigmentosa, a condition that leads to gradual vision loss. When Ms. Siddiqui’s mother was in her 30s, she began going blind. Last summer, Ms. Siddiqui told a podcast host that...
By Amanda Hess, The New York Times | 04.05.2025
Image "Elon Musk" by Debbie Rowe on Wikimedia Commons licensed under CC by S.A. 3.0
For months, an internet-wide guessing game has swirled around the question of where Elon Musk’s intelligence falls on the bell curve. President Trump has called...
By Peter Wehling, Tino Plümecke, and Isabelle Bartram
| 03.26.2025
This article was originally published as “Soziogenomik und polygene Scores” in issue 272 (February 2025) of the German-language journal Gen-ethischer Informationsdienst (GID); translated by the authors.
In mid-November 2024, the British organization Hope not Hate published its investigative research ‘Inside the Eugenics Revival’. In addition to documentating an active international “race research” network, the investigation also brought to light the existence of a US start-up that offers eugenic embryo selection. Heliospect Genomics aims to enable wealthy couples to...
By Dalton Conley, The New York Times | 03.13.2025
Since Francis Galton coined the phrase “nature versus nurture” 150 years ago, the debate about what makes us who we are has dominated the human sciences.
Do genes determine our destiny, as the hereditarians would say? Or do we enter...